Temperature Changing the temperature can also affect equilibrium position If we increase the temperature, according to Le Châtelier's Principle the equilibrium will act to reduce the temperature How it does this and whether it favours the reactants or\(\text{AB}_{2}\) is produced through the forward reaction Le Chatelier's principle states that if the temperature is increased the equilibrium will change to decrease the temperature of the vessel That is the reaction that takes in heat (endothermic) will be favouredGeneral Chemistry II Lab #8 – Le Chatelier's Principle The Effect of Temperature on Equilibrium INTRODUCTION Le Chatelier's Principle states that if a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change of conditions, reactions occur in the system that
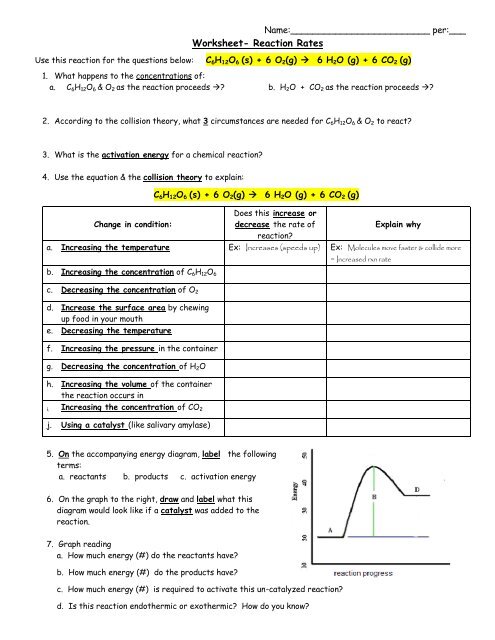
Worksheet Reaction Rates Le Chatelier
Le chatelier's principle temperature graph
Le chatelier's principle temperature graph-They help reactions achieve equilibrium fasterLe Châtelier's Principle When a stress is applied to a system at Equilibrium, the system readjusts so as to relieve or offset the stress Stress is any imposed factor which upsets the balance in rates between the forward and reverse reactions


Le Chatelier S Principle Ppt Download
A state in which opposing forces or influences are balanced aA bB cC dD reactants products An expert on stressing equilibrium!Thus the effect of change of temperature on the two reactions is different By LeChatelier's principle for an exothermic reaction at equilibrium lowering of temperature will favour the forward reaction And for an endothermic reaction, an increase in temperature will favour the forward reaction Effect of the Catalyst on the Chemical EquilibriumLe Chatelier's principle, also called Chatelier's principle, is a principle of chemistry used to predict the effect of a change in conditions on chemical equilibria The principle is named after French chemist Henry Louis Le Chatelier, and sometimes also credited to Karl Ferdinand Braun, who discovered it independently It can be stated as When any system at equilibrium for a long period of time is subjected to a change in concentration, temperature
A worked example using Le Chatelier's principle to predict how concentrations will shift for different perturbations Example includes changing reaction vessel volume, changing amount of solid product, adding inert gas, and adding a catalystStep 4 Was the temperature increased or decreased?Le Chatelier's Principle Tutorial Key Concepts In 14, the French Chemist Henri Le Chatelier suggested that equilibrium systems tend to compensate for the effects of
Changing the temperature of a system at equilibrium has a different effect A change in temperature actually changes the value of the equilibrium constant However, we can qualitatively predict the effect of the temperature change by treating it as a stress on the system and applying Le Chatelier's principleLe Chateliers Principle Temperature Graph Monday, 16 December 19 Add Comment Le Chateliers Principle H1carbonq1 Lino General Scheme For Pressure Temperature Phase Diagram Of Equilibrium Written Response Le Chateliers Principle Chemical Equilibrium Siyavula HenryUsing Le Chatelier's Principle with a change of temperature For this, you need to know whether heat is given out or absorbed during the reaction Assume that our forward reaction is exothermic (heat is evolved) This shows that 250 kJ is evolved (hence the negative sign) when 1 mole of A reacts completely with 2 moles of B


Chem 40s Unit 4 Notes


Van T Hoff Equation Equilibrium Priyamstudycentre
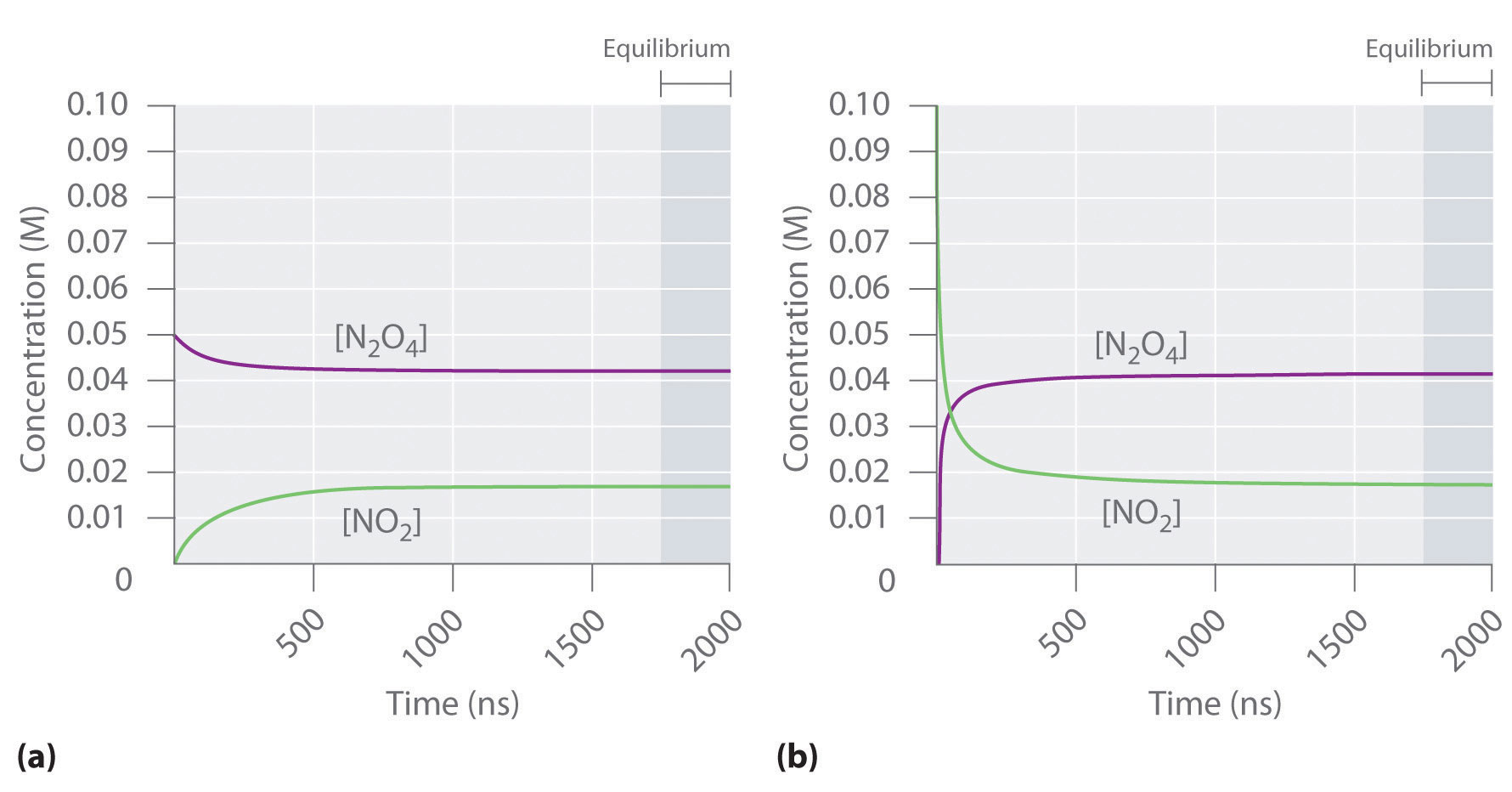
2 Effect of changes in temperature on an equilibrium system;Graphs and Le Chatelier's principle Graphs can be used to represent data about equilibrium reactions The following are some points to keep in mind when presented with a graph Identify the type of graph by looking at the label on the yaxis You will find either a ratetime graph a moletime or concentrationtime graphLe Chatelier's Principle In 14 the French chemist and engineer HenryLouis Le Chatelier proposed one of the central concepts of chemical equilibria Le Chatelier's principle can be stated as follows A change in one of the variables that describe a system at equilibrium produces a shift in the position of the equilibrium that counteracts the effect of this change
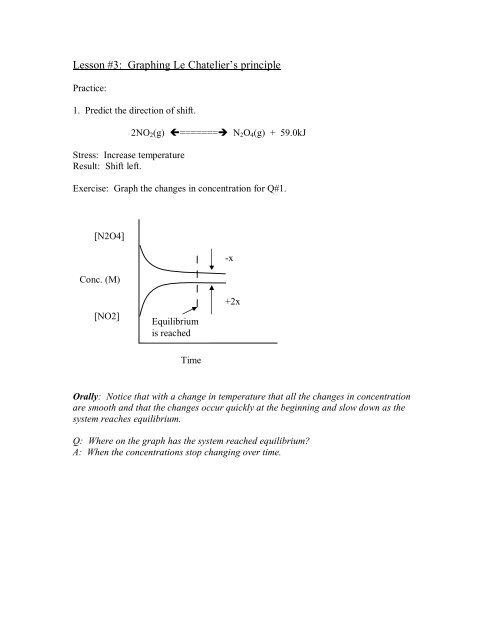


Lesson 3 Graphing Le Chatelier S Principle
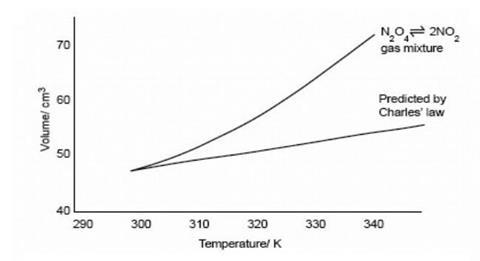


The Effect Of Pressure And Temperature On Equilibrium Le Chatelier S Principle Experiment Rsc Education
Le Chatelier's Principle A dynamic equilibrium tends to respond so as to relieve the effect of any change in the conditions that affect the equilibrium http//wwwyoutubecom/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=7zuUV455zFs 1 Changing Concentration of Reactants or Products • Addition of a substance (either reactant or product)Le Chatelier's Principle can be summarised as A chemical system in equilibrium will always attempt to resist any external change imposed onto it The external changes that affect chemical systems in equilibrium are related to concentrations, pressure (or volume) of gases, and temperature changesLe Chatelier's Principle In the graph to the left, Temperature Change When energy is either added or removed, the equilibrium shifts to minimize the change in energy (Depends on whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic) The system below is being cooled



Le Chatelier S Principle Ppt Download



Le Chatlier S Principle Interpreting Graphs Youtube
Le Chatelier's Principle It is possible to shift the position of an equilibrium so that either reactants or products are favoured In order to decide how to alter equilibrium conditions to produce the desired effect you must first understand Le Chatelier's PrincipleStep 3 Are both rates affected equally?Le Chatelier's principle addresses how an equilibrium shifts when the conditions of an equilibrium are changed The direction of shift can be predicted for changes in concentrations, temperature, or pressure Catalysts do not affect the position of an equilibrium;


Chm 1046


Solved Le Chatelier S Principle Graphs Looking At Concentration Changes Course Hero
Le Chatelier's Principle states that 'if a system at equilibrium is disturbed, then the system adjusts itself so as to minimise the disturbance' An increase in pressure causes a system to go in the direction where there are less particles In system 1, there are the same number of particles on each side of the equationLe Chatelier's principle Worked example Introduction to reaction quotient Qc The reaction quotient Q Comparing Q vs K example Practice Using Le Chatelier's principle This is the currently selected item Comparing Q vs K example Our mission is to provide a free, worldclass education to anyone, anywhereSafety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators



Reversible Reactions Equilibrium And Le Chatelier S Principle Compound Interest



Le Chatelier S Principle
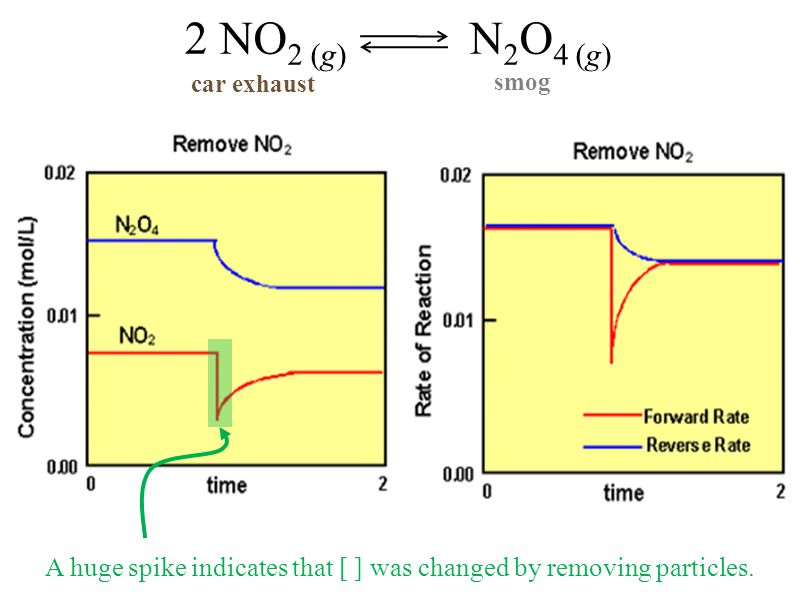
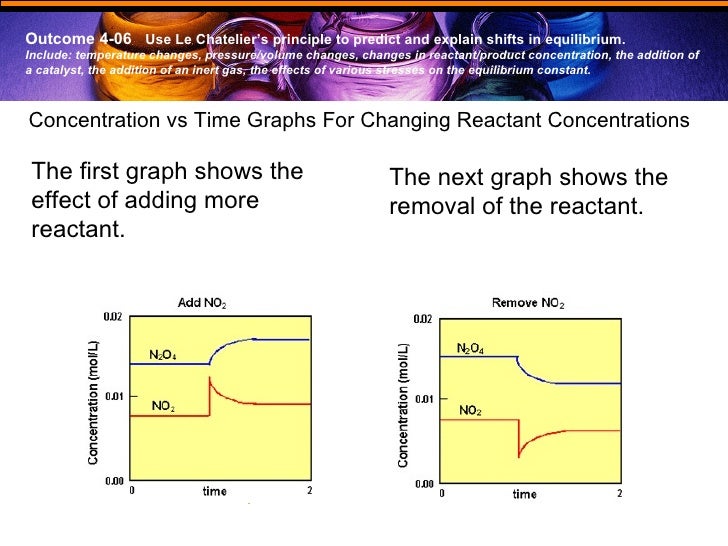
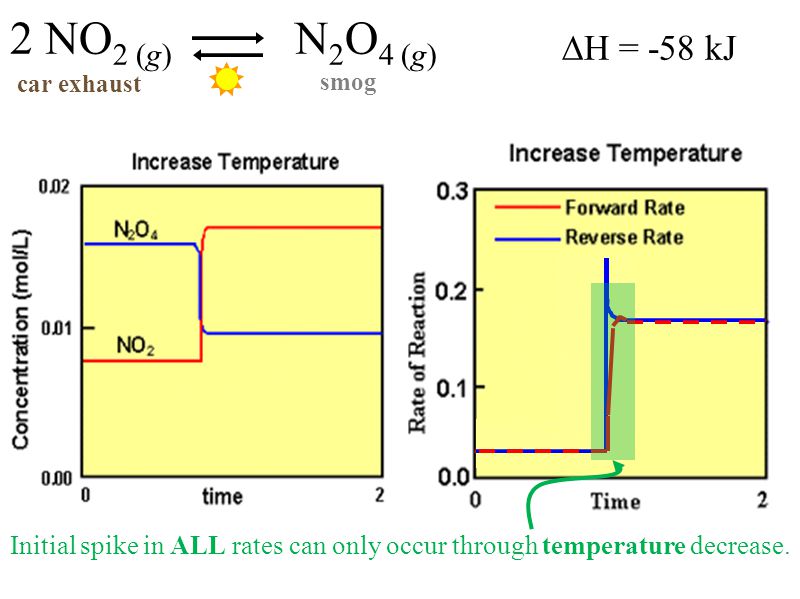
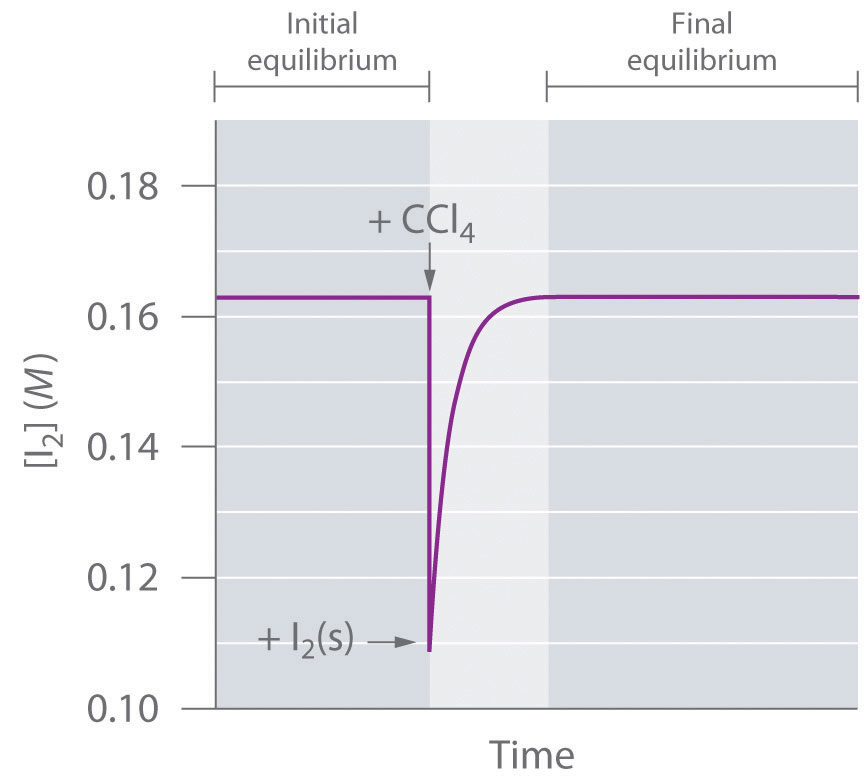
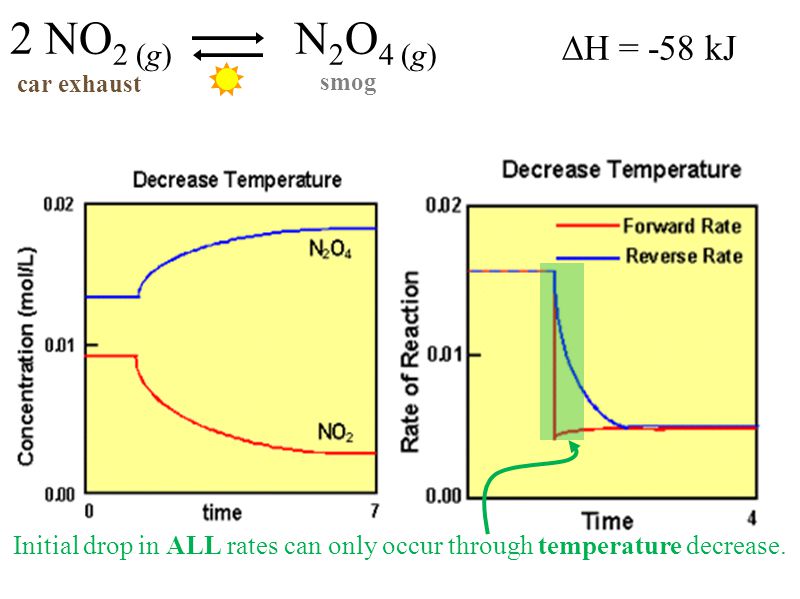
On the graph, show how the equilibrium is affected by the addition of iodine 2) Change in volume of a gas phase system (C=n/V)if the volume of a container is increased, then the concentration of all substances is initially decreased (and vice versa) Example 2 SO 2(g) O 2(g) ⇆ 2 SO 3(g) The reaction favors the products On the graph, show how theHow do you graph Le Chatelier's principle?Notes on Graphs Involving LeChatelier's Principle 1 Temperature Changes • no sudden changes in concentration of any species, therefore no vertical lines on the graph Example N2O4 (g) heat ⇆ 2 NO2 (g) Let's say that the system is at equilibrium at a certain temperature


Chemistry Equilibrium Le Chateliers Principle Temperature And Catalysts



C3 5 Production Of Ammonia An Example Of A Reversible Reaction Secondary Science 4 All
3 Factors that affect the position of equilibriumApplying Le Chatelier's Principle to Saturated Solutions Solubility tables like the one above, tell us the maximum mass of solute that will dissolve in a given mass of solvent under certain conditions Typically, the conditions are a temperature of 25 o C and a pressure of 1013 kPa (1 atm) Let's see what happens when we change either of these conditionsTemperature change (exothermic and endothermic), concentration change, volume change of gaseous systems A According to Le Chatelier's Principle, processes will occur that tend to counteract that change Thus, if there is a temperature change, processes will occur that tend to recover the temperature change


Chemistry Equilibrium Le Chateliers Principle Temperature And Catalysts
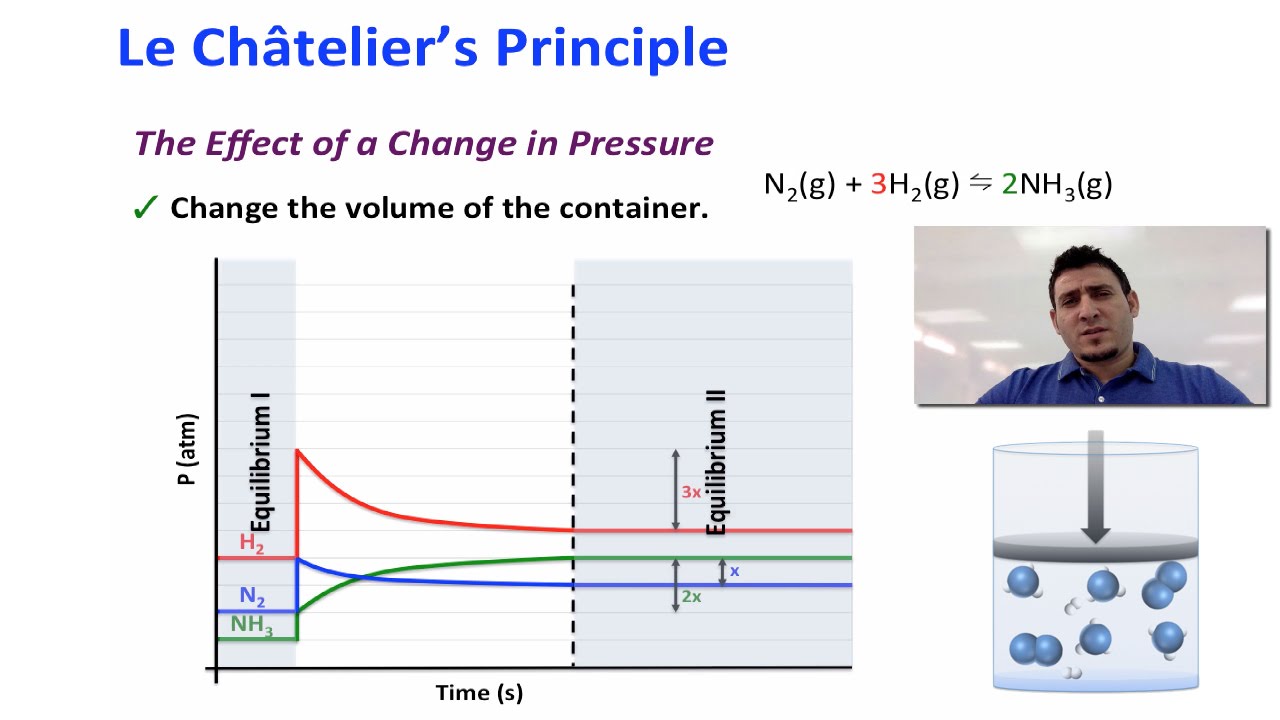


Chemical Equilibrium Le Chatelier S Principle Youtube
Chemistry Chemical Equilibrium Le Chatelier's principle 1 Answer Dr Hayek Aug 24, 16 Watch this video Explanation I recommend the following video that will show you how to draw the graph of concentration profile using Le Châtelier's principle ChemicalChanging concentrations The facts Equilibrium constants aren't changed if you change the concentrations of things present in the equilibrium The only thing that changes an equilibrium constant is a change of temperature The position of equilibrium is changed if you change the concentration of something present in the mixture According to Le Chatelier's Principle, the71 Le Chatelier's principle Applications and skills Application of Le Châtelier's principle to predict the qualitative effects of changes of temperature, p
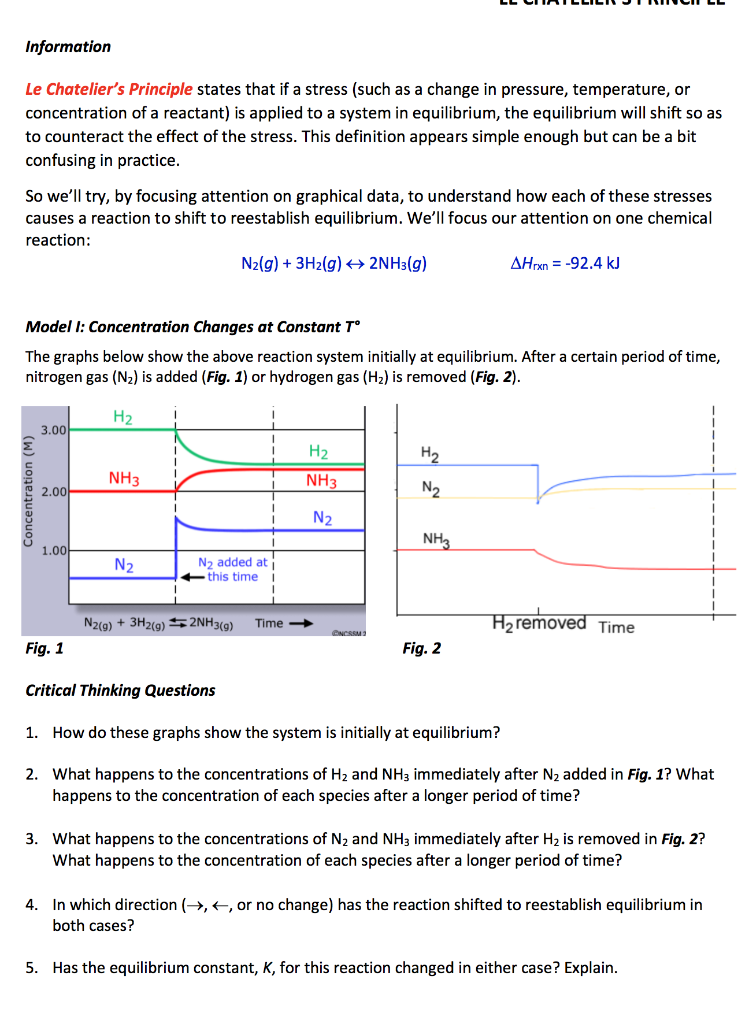


Solved Information Le Chatelier S Principle States That I Chegg Com



Lesson Worksheet Le Chatelier S Principle Nagwa
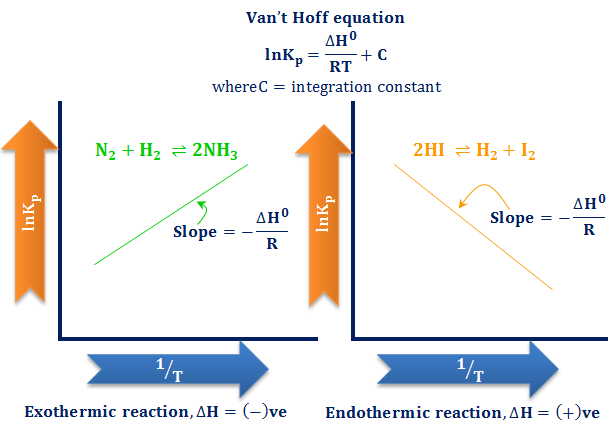
In accordance with Le Chatelier's principle, the equilibrium constant changes to minimize the change in temperature For endothermic reactions, an increase in temperature can be minimized by utilizing some of the heat to convert reactants to products, shifting the equilibrium to the right side of the reaction and increasing the value of KAs the temperature is increased, the endothermic path is preferred, according to Le Châtelier's Principle This direction absorbs heat in order to alleviate the discomfort caused by temperature changesThe new K value is greater than the old K value since this is an endothermic reaction To achieve this higher K value, the system shifts to produce more product and consume moreStep 2 Are the rates both affected in the same way or is one rate increased and the other decreased when the stress is applied?



Chemical Equilibrium Le Chatelier S Principle Youtube



Le Chatelier S Principle
You'll have to add weight to the other side to regain balance Chemical reactions make the same sorts of adjustments automatically, and Le Châtelier's principle will help us to understand it Le Châtelier's principle is named for Henry Louis Le Châtelier, a French chemist who died in 1936 at the age of 85 Versions of Le Châtelier's principal are used in economics to predict the directionLe Chatelier's principle can be used to predict the behavior of a system due to changes in pressure, temperature, or concentration Le Chatelier's principle implies that the addition of heat to a reaction will favor the endothermic direction of a reaction as this reduces the amount of heat produced in the systemBasic Le Chatelier's Principles are applied to help gain oxygenated hemoglobin (or blood) as well as to transport oxygen to areas of the body that lack oxygen Finally looking upon our graph we can conclude that around 85% the partial pressure no long effects the curve and the system establishes equilibrium
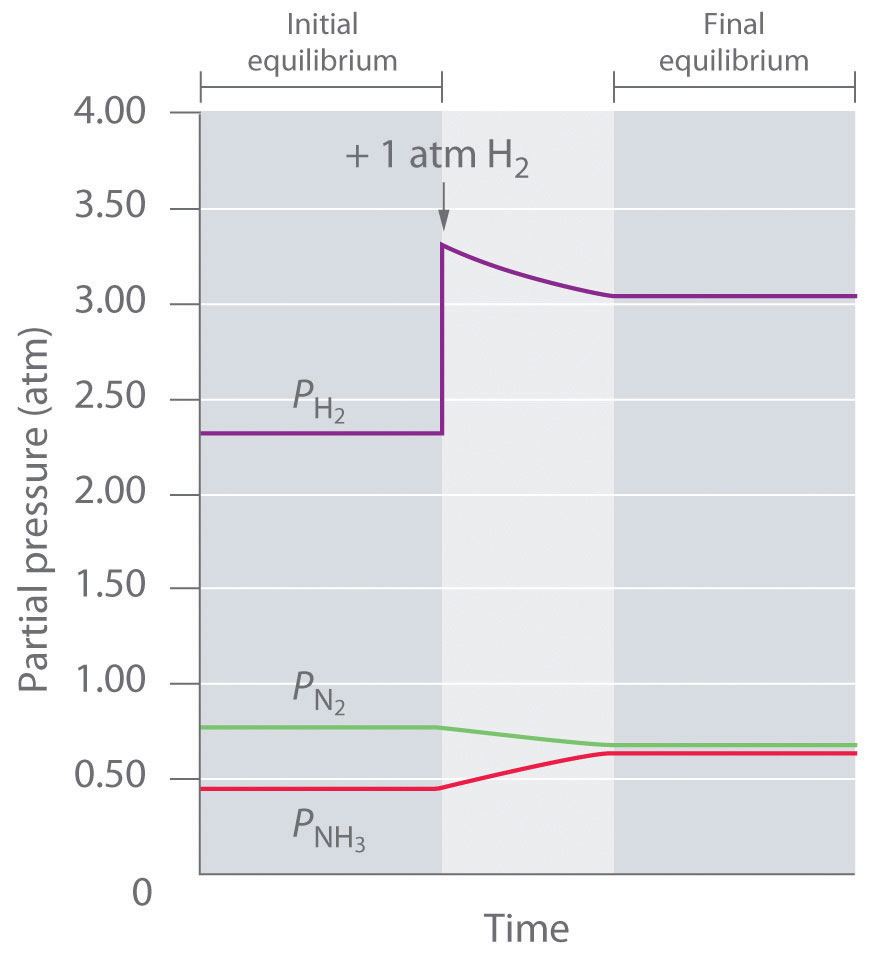


Factors That Affect Equilibrium


Le Chatelier S Principle Chart Worksheet Answer Key Ganada
Le Chateliers PrincipleLe Chateliers PrincipleIf a dynamic equilibrium is disturbed by changingthe conditions, the position of equilibrium moves tocounteract the change 2 Change in concentrationSuppose you have an equilibrium established between foursubstances A, B, C and DWhat would happen if you changed the conditions byincreasing the concentration of A?By Le Chatelier's principle, the system will act to consume some of the products to reduce the rate of collision and also the reverse reaction rate Concentration of reactants will increase which increases the rate of forward reaction Equilibrium is reached when forward reaction rate equals reverse reaction rate Pressure/volumeLe Châtelier's principle, chemical principle that states that if a system in equilibrium is disturbed by changes in determining factors, such as temperature, pressure, and concentration of components, the system will tend to shift its equilibrium position so as to counteract the effect of the disturbance (see chemical equilibrium)



Hsc Chemistry Le Chatelier Principle And Equilibrium Guide



Increasing Temperature In System Of Dynamic Equilibrium Chemistry Stack Exchange
Step 1 Check the axes so that you know what the variables are on this graph;The effect of temperature on solubility can be explained on the basis of Le Chatelier's Principle Le Chatelier's Principle states that if a stress (for example, heat, pressure, concentration of one reactant) is applied to an equilibrium, the system will adjust, if possible, to(Use Le Chatelier's principle)


Phase Diagrams



Le Chatelier S Principle Chemical Equilibrium Siyavula
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy &According to Lechatelier's principle a change in temperature is a stress on an equilibrium system If at equilibrium the temperature of system is changed the system will no longer at remain at equilibrium To restore equilibrium, the reaction will in either forward or backward directionLe Chatelier's Principle If a reaction is at equilibrium and we alter the conditions so as to create a new equilibrium state, then the composition of the system will tend to change until that new equilibrium state is attained(We say tend to change because if the reaction is kinetically inhibited, the change may be too slow to observe or it may never take place)
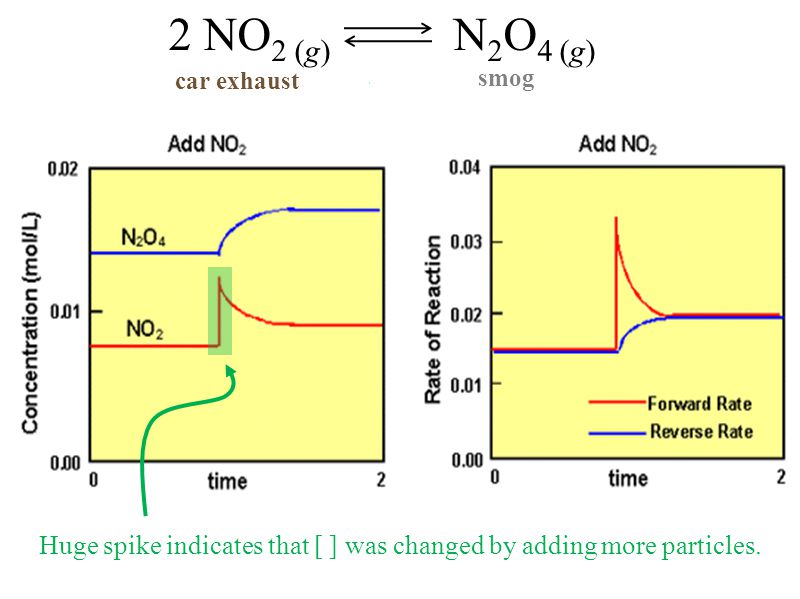


Le Chatelier S Principle Ppt Download



Le Chatelier S Principle Chemical Equilibrium Siyavula
Le Chatelier′s Principle is the principle when a stress is applied to a chemical system at equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift to relieve the stressIn other words, it can be used to predict the direction of a chemical reaction in response to a change in conditions of temperature, concentration, volume, or pressureWhile Le Chatelier's principle can be used to predict theIn terms of chemical equilibrium, stress means change and in a system it includes changes in quantities of reactants or products changes in volume1 Le Chatelier's principle – Introduction;


Chemical Equilibria When Initially Looking At Reaction We Often Assume That They Go To Completion That Is To Say That As Much Product Is Formed As It Allowed By The Reactants That Are Given In Reality Most Reactions Do Not Go To 100 Completion Instead They



Dynamic Equilibrium Graph Page 1 Line 17qq Com
Le Chatelier's Principle Introduction In this experiment you will observe shifts in equilibrium systems when conditions such as concentration and temperature are changed You will explain the observed color changes of four reactions in terms of Le Chatelier's principle Le Chatelier predicted how an equilibrium system would respond toLe Chatelier's Principle The Effect of Temperature on Equilibrium Le Chatelier's Principle states that if a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change of conditions, reactions occur in the system that tend to counteract the imposed change In other words, the system tends to react in a way that restores the equilibrium When the imposed stressLe Chatelier's principle predicts that the equilibrium will move to the right with an increase in temperature as the forward reaction is endothermic The brown colour intensifies The equilibrium constant, K p , has a value of 48 atm at 400 K (127 °C), and the equilibrium will lie almost completely over to the right at 140 °C


Chemistry Equilibrium Le Chateliers Principle Temperature And Catalysts



Worksheet Reaction Rates Le Chatelier


Chemistry Equilibrium 10



Equilibrium Shift Graph Chemistry Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Hsc Chemistry Module 5 Inquiry Question 2



Hsc Chemistry Le Chatelier Principle And Equilibrium Guide



Climate Change Feedback Wikipedia



Le Chatelier S Principle Chemical Equilibrium Siyavula


Shifting Equilibria Le Chatelier S Principle Chemistry For Majors



Le Chatelier Principle And Effect Of Temperature Pressure And Concentration On The Equilibrium Of A Ch Le Chatelier S Principle Teaching Chemistry Principles
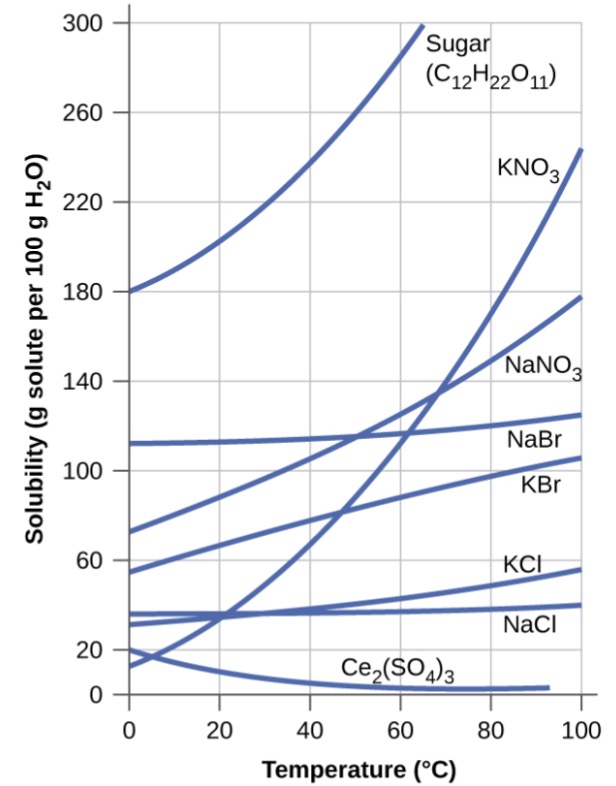


Solubility Of Gases And Solids In Liquids Chemistry Class 12 Solutions
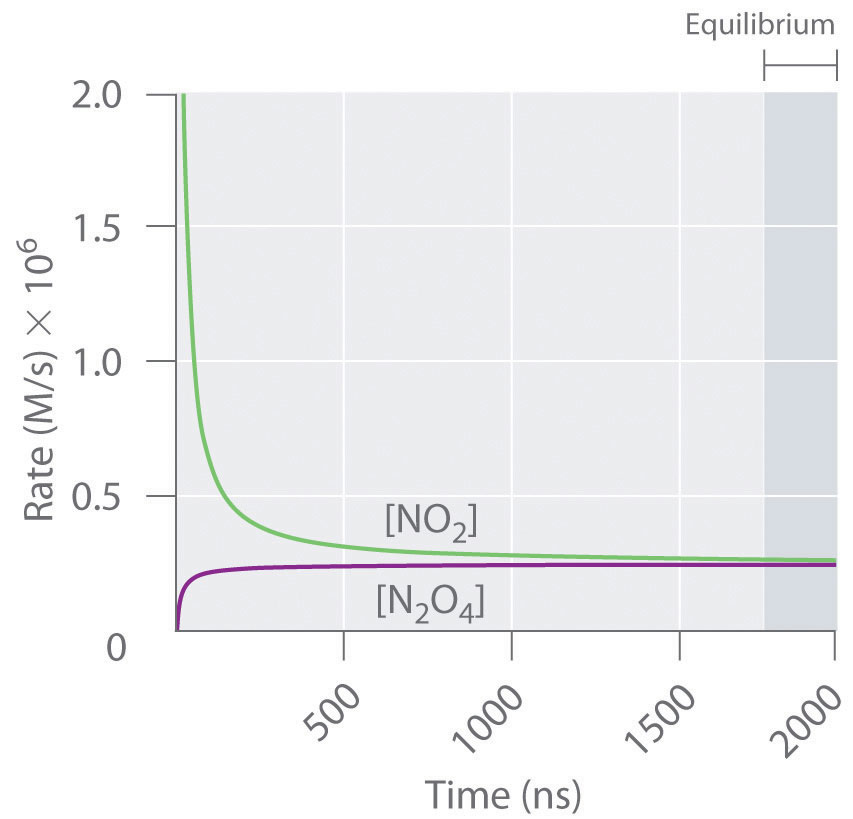


Chemical Equilibrium


Chemistry Equilibrium Le Chateliers Principle Temperature And Catalysts



Rate Time Graphs Chemical Equilibrium


Storing Carbon Dioxide


Le Chatelier S Principle Ppt Download


Chemistry Equilibrium Le Chateliers Principle Temperature And Catalysts



8 3 Le Chatelier S Principle Chemistry Libretexts


Factors That Affect Equilibrium



The Changes In Concentration Pressure Volume And Temperature Can Change The Equilibrium Position Explain



Le Chatelier S Principle Chemical Equilibrium Siyavula



Le Chatelier S Principle Chemical Equilibrium Siyavula



7 1 Le Chatelier S Principle Changes In Concentration Sl Youtube



Savvy Chemist Equilibrium 1 Applying Le Chatelier S Principle



Graphs And Le Chatelier S Principle Chemical Equilibrium



Le Chateliers Principle Siyavula Textbooks Grade 12 Physical Science Openstax Cnx


Le Chatelier S Principle Ppt Download


Le Chatelier S Principle Davidcalvin



Hsc Chemistry Le Chatelier S Principle Science Ready



Chemical Equilibrium Acids And Bases Applying Le Chatelier S Principle To Acid Base Equilibrium Ppt Download


Chemical Equilibrium


Le Chatelier S Principle Davidcalvin


Chemistry Equilibrium Le Chateliers Principle Temperature And Catalysts
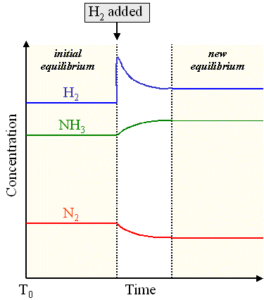


Le Chatelier S Principle Statement Explanation And Examples



Chemistry The Central Science Chapter 15 Section 6


Dyn Eqm Notes


5 11 Practical Obtain A Temperature Time Graph To Show The Constant Temperature During A Change Of State Tutormyself Chemistry



Difference Between Static And Dynamic Equilibrium Biology Dictionary



Le Chatelier S Principle Chemical Equilibrium Siyavula
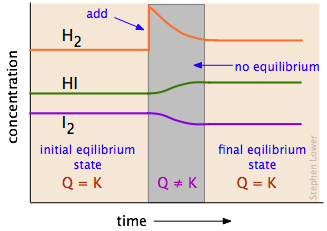


11 2 Le Chatelier S Principle Chemistry Libretexts



Controlling The Products Of Reactions
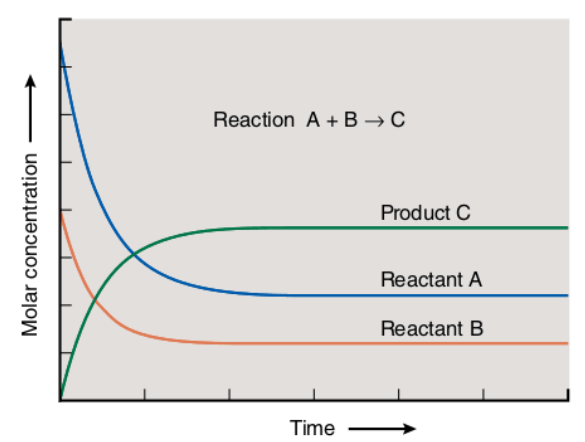


Dynamic Equilibrium A Level Chemistry Revision Notes
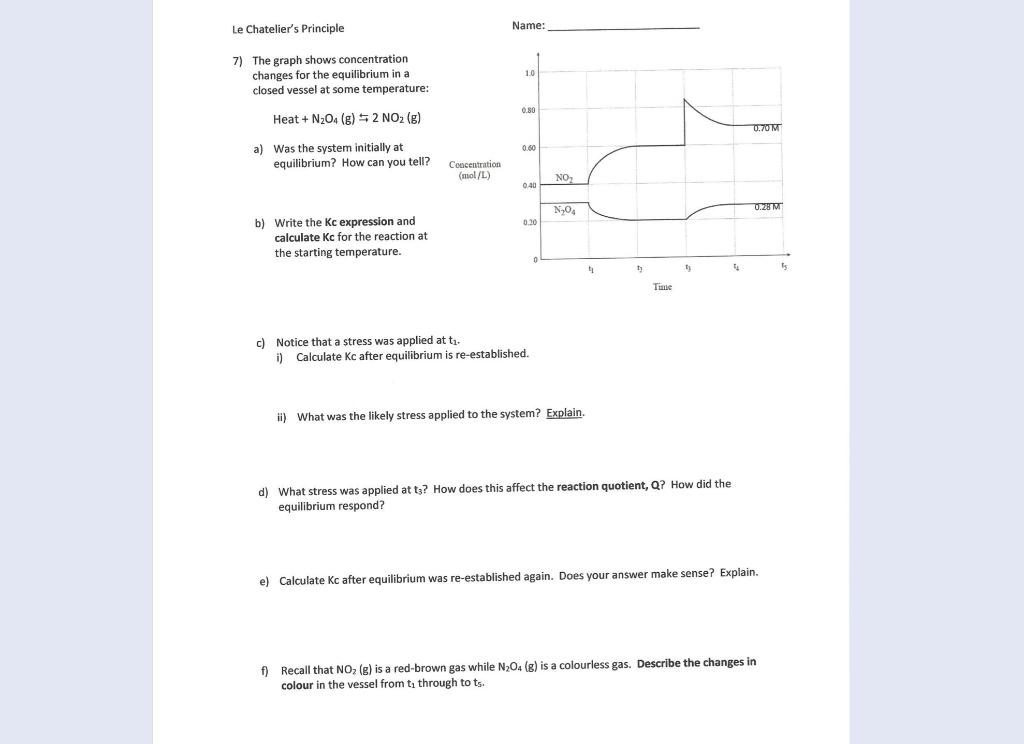


Solved Le Chatelier S Principle Name 7 The Graph Shows Chegg Com


Chemistry Equilibrium Le Chateliers Principle Temperature And Catalysts



Hsc Chemistry Le Chatelier Principle And Equilibrium Guide


Le Chatelier S Principle Davidcalvin


Le Chatelier S Principle



Le Chatelier S Principle Applications Adichemistry



Water Gas Shift Reaction Wikipedia
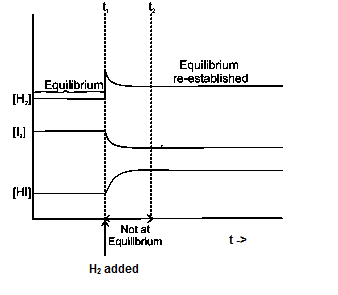


Le Chatelier S Principle Effect Of Temperature Pressure Concentration And Catalyst



Equilibrium Graphs Temperature Change Youtube



Le Chatelier S Principle
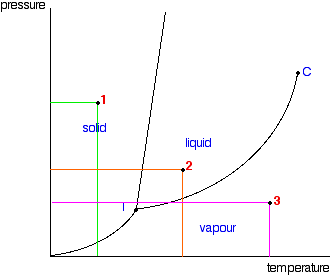


Phase Diagrams Of Pure Substances
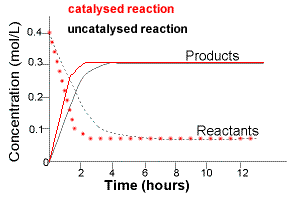


Chemical Equilibrium Concepts Chemistry Tutorial
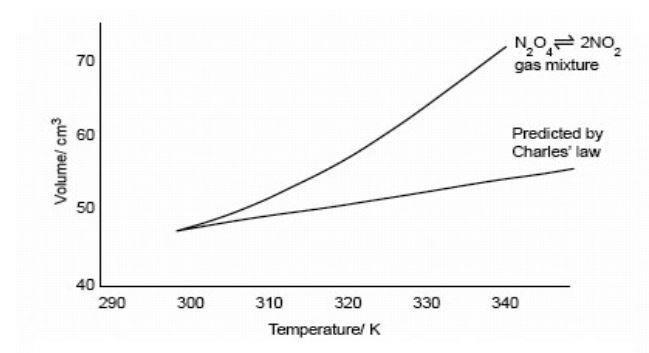


The Effect Of Pressure And Temperature On Equilibrium Le Chatelier S Principle Experiment Rsc Education



Quiz 3 Yield Graphing Lechatelier S Principle
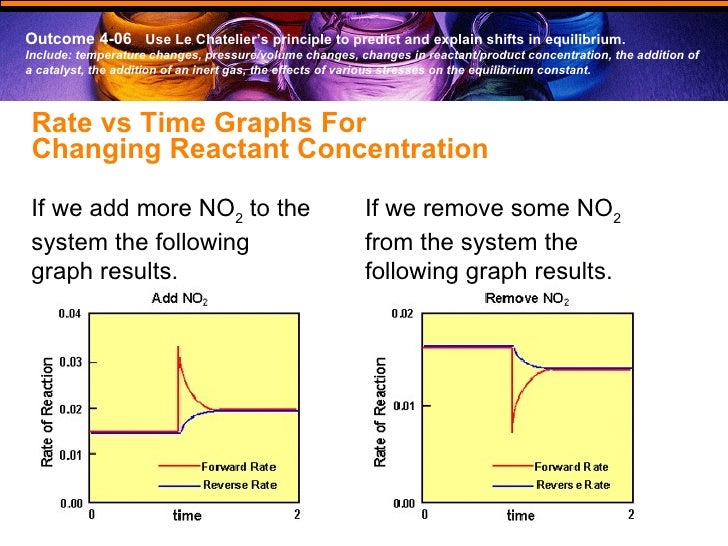


Chem 40s Unit 4 Notes



8 3 Le Chatelier S Principle Chemistry Libretexts



Aucun commentaire:
Publier un commentaire